You are using a browser that is not supported by this site. The site will not function properly. Please switch to the latest version of a supported browser such as Chrome, Safari, Edge, or Firefox to use this site.

Understanding PAH
What is PAH?
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH; WHO Group 1) is a narrowing of the arteries that carry blood from the heart to the lungs.
When the arteries near your heart narrow, this can cause:
- Extra strain on the heart, making it work harder to deliver blood to the lungs
- Increases in pressure—known as hypertension—in the blood vessel (called the pulmonary artery) that delivers blood to your lungs
- Symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue when doing activities
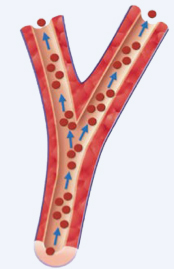
Healthy vessel:
Blood can be pumped easily from the heart to the lungs.
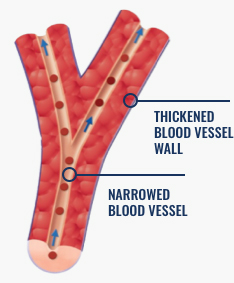
Vessel with PAH:
Narrow vessels slow down the flow of blood and make the heart work harder to pump blood to the lungs.
As PAH worsens, the right side of your heart has to work even harder to pump blood to your lungs. This can lead to difficulty with breathing and fatigue that may make it tougher to carry out everyday tasks such as getting dressed, climbing stairs, or walking to the mailbox.
WHY ARE THE PAH PATHWAYS IMPORTANT?
PAH makes it harder to breathe, and this has to do with how hard the right side of your heart needs to work to pump blood to your lungs. This is caused by an imbalance of 1 or more of 3 natural substances in your body:



PAH medications work to correct this imbalance. When your body generates the right amount of each substance, your blood vessels stay open and function properly.
You can learn more about the 3 pathways, including prostacyclin, by visiting the PAH Initiative website.
What are the symptoms of PAH?
Below are some common symptoms of PAH you might experience:
Dizziness and/or fainting
Feeling tired or worn out
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Swollen abdomen
Swollen ankles and legs
To help manage your PAH symptoms, your doctor will assess your risk status and will work with you to develop a care plan.
Learn more about the role of risk assessment in managing PAH.
Learn MoreWhere can I find additional information on PAH?
Find information and support about PAH from the Pulmonary Hypertension Association (PHA) community. Visit phassociation.org to:
- Connect with others
- Join a support group
- Find information for caregivers
- Find a doctor or PAH specialist in your area who has pump experience
- Discover additional support and resources

Learn more about PAH and explore helpful resources to help you navigate life with PAH. Visit PAHinitiative.com
Learn more about the work being done to increase awareness and innovation in finding a cure for PAH. Visit PHAware.global
Seek out other patients. I highly recommend joining a local support group to meet others with PAH. They can share tips and knowledge or just be a shoulder to lean on.
Remodulin® (treprostinil) Injection
Important Safety Information for Remodulin
Before you take Remodulin, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- Have other medical conditions or take other medicines that may affect your use of Remodulin by increasing the risk of side effects or decreasing the drug’s effectiveness.
- Have liver or kidney problems. Your Remodulin dose may need to be adjusted if you have liver problems.
- Have low blood pressure or bleeding problems.
- Are taking gemfibrozil (for high cholesterol), rifampin (for infection) or other drugs that affect liver enzymes. Your doctor may need to adjust your Remodulin dosage.
- Are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if Remodulin will harm your unborn baby or if Remodulin passes into your breast milk.
What are the serious side effects of Remodulin?
- Continuous intravenous (IV) infusions of Remodulin delivered using an external infusion pump, with a tube placed in a central vein within the chest, are associated with the risk of blood stream infections and sepsis, which may be fatal. Therefore, continuous subcutaneous (SC) infusion delivered just beneath the skin is the preferred type of delivery.
- Worsening of PAH symptoms. Do not stop taking or greatly reduce your Remodulin dose without consulting your doctor.
- Low blood pressure (symptomatic hypotension). If you have low blood pressure or are taking drugs that lower your blood pressure, the risk of low blood pressure is increased.
- Bleeding problems. Remodulin may increase the risk of bleeding in people who take blood thinners (anticoagulants).
What are the possible side effects of Remodulin?
- In clinical studies of SC infusion of Remodulin, most people experienced infusion site pain and infusion site reaction (redness, swelling, and rash). These symptoms were sometimes severe and sometimes required treatment with narcotics or discontinuation of Remodulin.
- IV infusion of Remodulin delivered through an external pump has been associated with the risk of blood stream infections, arm swelling, tingling sensations, bruising, and pain.
- The most common side effects seen with either SC or IV Remodulin were headache, diarrhea, nausea, rash, jaw pain, widening of the blood vessels (vasodilatation), and swelling from fluid retention (edema). These are not all the possible side effects of Remodulin. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/MedWatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may report side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/MedWatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
The risk information provided here is not comprehensive.
What is Remodulin?
Remodulin is a prescription medication used to treat adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH; WHO Group 1), which is high blood pressure in the arteries of your lungs. Remodulin can reduce symptoms associated with exercise. Remodulin was studied mainly in patients with NYHA Functional Class II-IV symptoms. It is not known if Remodulin is safe and effective in children.
In people with PAH who need to switch from epoprostenol, Remodulin is approved to slow the worsening of symptoms.
REMISIconMAY2021
To learn more about Remodulin, talk with your healthcare provider. Please see Full Prescribing Information at www.remodulin.com or call Customer Service at 1-877-UNITHER (1-877-864-8437).
To learn more about Remodulin, talk with your healthcare provider. Please see Full Prescribing Information at www.remodulin.com or call Customer Service at 1-877-UNITHER (1-877-864-8437).
PAH=pulmonary arterial hypertension; WHO=World Health Organization.
Remodulin® (treprostinil) Injection
Important Safety Information for Remodulin
Before you take Remodulin, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- Have other medical conditions or take other medicines that may affect your use of Remodulin by increasing the risk of side effects or decreasing the drug’s effectiveness.
- Have liver or kidney problems. Your Remodulin dose may need to be adjusted if you have liver problems.
- Have low blood pressure or bleeding problems.
- Are taking gemfibrozil (for high cholesterol), rifampin (for infection) or other drugs that affect liver enzymes. Your doctor may need to adjust your Remodulin dosage.
- Are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if Remodulin will harm your unborn baby or if Remodulin passes into your breast milk.
What are the serious side effects of Remodulin?
- Continuous intravenous (IV) infusions of Remodulin delivered using an external infusion pump, with a tube placed in a central vein within the chest, are associated with the risk of blood stream infections and sepsis, which may be fatal. Therefore, continuous subcutaneous (SC) infusion delivered just beneath the skin is the preferred type of delivery.
- Worsening of PAH symptoms. Do not stop taking or greatly reduce your Remodulin dose without consulting your doctor.
- Low blood pressure (symptomatic hypotension). If you have low blood pressure or are taking drugs that lower your blood pressure, the risk of low blood pressure is increased.
- Bleeding problems. Remodulin may increase the risk of bleeding in people who take blood thinners (anticoagulants).
What are the possible side effects of Remodulin?
- In clinical studies of SC infusion of Remodulin, most people experienced infusion site pain and infusion site reaction (redness, swelling, and rash). These symptoms were sometimes severe and sometimes required treatment with narcotics or discontinuation of Remodulin.
- IV infusion of Remodulin delivered through an external pump has been associated with the risk of blood stream infections, arm swelling, tingling sensations, bruising, and pain.
- The most common side effects seen with either SC or IV Remodulin were headache, diarrhea, nausea, rash, jaw pain, widening of the blood vessels (vasodilatation), and swelling from fluid retention (edema). These are not all the possible side effects of Remodulin. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/MedWatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
The risk information provided here is not comprehensive.
What is Remodulin?
Remodulin is a prescription medication used to treat adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH; WHO Group 1), which is high blood pressure in the arteries of your lungs. Remodulin can reduce symptoms associated with exercise. Remodulin was studied mainly in patients with NYHA Functional Class II-IV symptoms. It is not known if Remodulin is safe and effective in children.
In people with PAH who need to switch from epoprostenol, Remodulin is approved to slow the worsening of symptoms.
REMISIconMAY2021
To learn more about Remodulin, talk with your healthcare provider. Please see Full Prescribing Information at www.remodulin.com or call Customer Service at 1-877-UNITHER (1-877-864-8437).
PAH=pulmonary arterial hypertension; WHO=World Health Organization.